- Comparing Quantities: We are often required to compare two quantities, in our daily life. They may be heights, weights, salaries, marks etc. To compare two quantities, their units must be the same.
- We are often required to compare two quantities in our daily life. They may be heights, weights, salaries, marks etc.
- While comparing heights of two persons with heights150 cm and 75 cm, we write it as the ratio 150 : 75 or 2 : 1.
- Ratio: A ratio compares two quantities using a particular operation.
- Percentage: Percentage are numerators of fractions with denominator 100. Percent is represent by the symbol % and means hundredth too.
- Two ratios can be compared by converting them to like fractions. If the two fractions are equal, we say the two given ratios are equivalent.
- If two ratios are equivalent then the four quantities are said to be in proportion. For example, the ratios 8 : 2 and 16 : 4 are equivalent therefore 8, 2, 16 and 4 are in proportion.
- A way of comparing quantities is percentage. Percentages are numerators of fractions with denominator 100. Per cent means per hundred. For example 82% marks means 82 marks out of hundred.
- Fractions can be converted to percentages and vice-versa. For example,
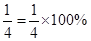 whereas,
whereas, 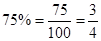
- Decimals too can be converted to percentages and vice-versa. For example,
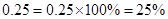
- Percentages are widely used in our daily life,
(a) We have learnt to find exact number when a certain per cent of the total quantity is given.
(b) When parts of a quantity are given to us as ratios, we have seen how to convert them to percentages.
(c) The increase or decrease in a certain quantity can also be expressed as percentage.
(d) The profit or loss incurred in a certain transaction can be expressed in terms of percentages.
(e) While computing interest on an amount borrowed, the rate of interest is given in terms of per cents. For example, ` 800 borrowed for 3 years at 12% per annum. - Simple Interest: Principal means the borrowed money.
- The extra money paid by borrower for using borrowed money for given time is called interest (I).
- The period for which the money is borrowed is called ‘Time Period’ (T).
- Rate of interest is generally given in percent per year.
- Interest (I):
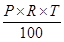
- Total money paid by the borrower to the lender is called the amount.
For More:-
CBSE Class–VII |
CHAPTER – 1 Integers | NMMS Revision Notes à
Click
Here
Tracing Changes Through a Thousand Years | NMMS Revision
Notes | Class 7 | Social à Click
Here
New Kings and Kingdoms | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 |
Social à Click Here
The Delhi Sultanate | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7
Social à Click
Here
The Mughal Empire | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Social à Click Here
Tribes Nomads and Settled Communities | NMMS Revision
Notes | Class 7 Social à
Click
Here
Devotional Paths to the Divine | NMMS Revision Notes |
Class 7 Social à
Click
Here
The Making of Regional Cultures | NMMS Revision Notes |
Class 7 Social à
Click
Here
Eighteenth Century Political Formations | NMMS Revision
Notes | Class 7 Social à
Click
Here
Environment | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Social à Click
Here
Inside Our Earth | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Social à Click Here
Our Changing Earth | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Social
à Click Here
Air | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Social à
Click Here
Water | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Social à Click Here
Human Environment Interactions the Tropical | NMMS
Revison Notes | Class 7 Social à
Click
Here
Life in the Deserts | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7
Social à Click Here
On Equality | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Social à Click Here
How the State Government Works | NMMS Revision Notes |
Class 7 Social à
Click
Here
Role of the Government in Health | NMMS Revision Notes |
Class 7 Social à
Click
Here
Growing up as Boys and Girls | NMMS Revision Notes |
Class 7 Social à
Click
Here
Women Change the World | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7
Social à Click Here
Understanding Media | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7
Social à Click Here
Markets Around Us | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Social à Click Here
A Shirt in the Market | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7
Social à Click Here
Nutrition in Plants | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7
Science à Click Here
Nutrition in Animals | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7
Science à Click Here
Heat | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Science à Click
Here
Acids Bases And Salts | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7
Science à Click Here
Physical And Chemical Changes | NMMS Revision Notes |
Class 7 Science à Click
Here
Respiration In Organisms | NMMS
Revision Notes | Class 7 Science à
Click
Here
Transportation in Animals and
Plants | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Science à Click
Here
Force and Pressure | NMMS
Quick Revision Notes | Class: 8 Physics à Click Here
Reproduction In Plants | NMMS
Revision Notes | Class 7 Science à
Click Here
Motion And Time | NMMS Revision
Notes | Class 7 Science à
Click Here
Electric Current and its
Effects | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Science à Click
Here
Light | NMMS Revision Notes |
Class 7 Science à
Click Here
Waste Water Story | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 7 Science
à Click Here
How When and Where | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 8 Social
à Click
Here
From Trade to Territory | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 8
Social à Click Here
Ruling the Countryside | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 8
Social à Click Here
Tribals Dikus and Vision of Golden Age | NMMS Revision
Notes | Class 8 Social à
Click
Here
When People Rebel | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 8 Social à Click Here
Weavers Iron Smelters and Factory Owners | NMMS Revision
Notes | Class 8 Social à
Click
Here
Civilising the Native Educating the Nation | NMMS
Revision Notes | Class 8 Social à
Click
Here
Women Caste and Reform | NMMS Revision Notes | Class 8
Social à Click Here





