Light Travels Along a Straight Line (VII)
Light is radiation or a form of energy that our eyes can detect. Light enables us to view our surroundings.
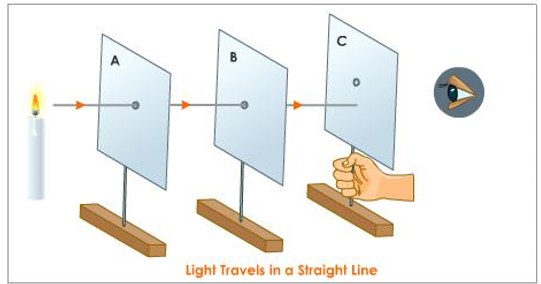
Light travels from one place to another in a straight line.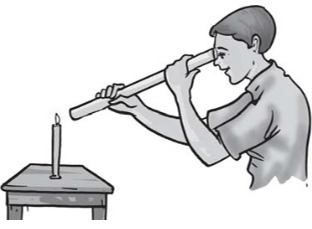
If you look at the flame of a candle with a straight pipe we can easily view the candle. However, if we bend the pipe we cannot view the candle and the light coming through it because it is blocked.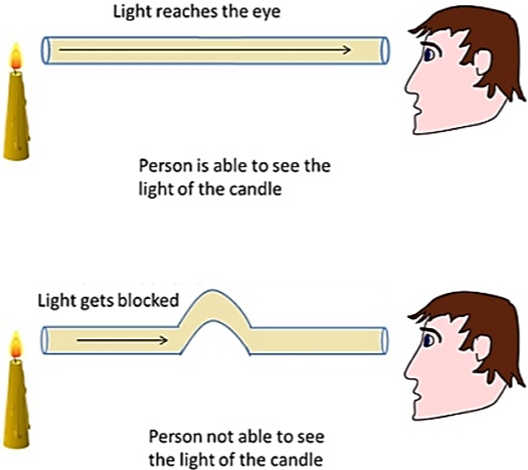
Reflection of Light (VII)
Reflection of light can be defined as the phenomenon of an object throwing back the light that falls on it. Hence, the reflection of light changes its path.
A mirror is generally any shiny surface that can reflect light. A mirror that has a plane surface is called a Plane Mirror.
A mirror that is curved, it either bulges in or out, is called a Curved Mirror.
The ray of light that falls on an object is called an incident ray and the ray of light which is sent back by an object is called a reflected ray.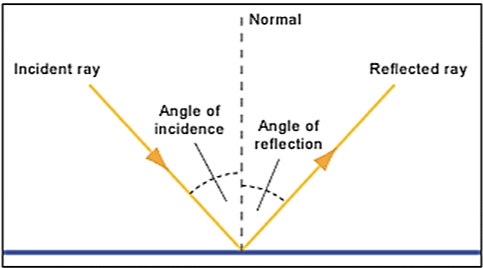
The image of an object can be defined as the impression of the object created by the light on the mirror. The distance between the image and the mirror, and the object and the mirror always remain the same.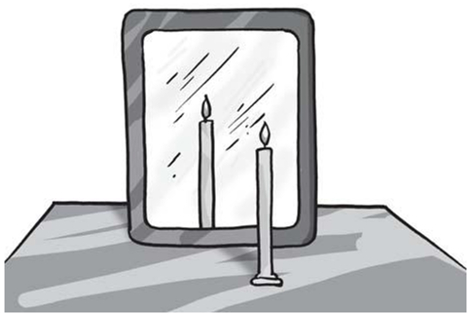
If we increase or decrease the distance between the object and the mirror, the distance between the image and the mirror also increases or decreases, respectively.
If the distance between the object and the mirror increases, the size of the image decreases and vice-versa.
An image is said to be erect if the image is formed the same side up as that of the object.
The image will be called Inverted if it is formed upside-down compared to the object.
Right or Left! (VII)
The image formed by the mirror is always left-right inverted. This means that the right side of the object appears as the left side of the image, and the left side of the object appears as the right side of the image.
We will find that in the mirror the ‘right’ appears ‘left’ and the ‘left’ appears ‘right’. Note that only sides are interchanged; the image does not appear upside down.
Lateral Inversion: The word ‘AMBULANCE’ is written in the manner as shown in the given image because in the mirror the ‘right’ appears ‘left’ and the ‘left’ appears ‘right’. This interchanging of the left and right sides of an object with its image is called lateral inversion.
Playing with Spherical Mirrors (VII)
A spherical mirror, as the name suggests, has a sphere-like shape. It appears as if it is a part of a sphere.
There are two types of spherical mirrors:
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
Concave Mirror - It is a spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards.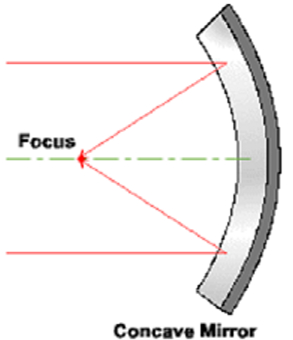
Convex Mirror: It is a spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved outwards.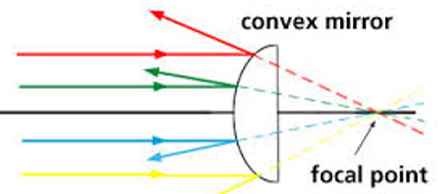
- Convex mirrors are used as rearview mirrors or side view mirrors in vehicles to see the traffic on the rear side of the road.
- The big convex mirrors are used as shop security mirrors.


Take a stainless steel spoon. If we bring the outer side of the spoon near our face and look into it, we see our image in it. If we increase the distance of the spoon from our face, we may see our image inverted. The curved shining surface of a spoon acts as a mirror. The inner surface of a spoon acts like a concave mirror, while its outer surface acts like a convex mirror.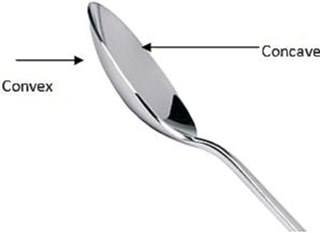
Take a rubber ball and cut a portion of it with a knife or a hacksaw blade. The inner surface of the cut ball is called concave and the outer surface is called convex.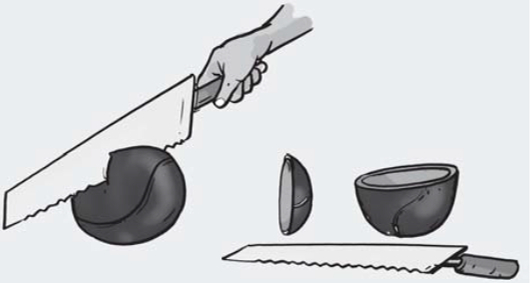
The Image formed by a Concave and Convex Mirror
| Real Image | Virtual Image |
| The real image is formed when the light rays reflect and meet at the same point. | A virtual image is formed when light rays reflect and diverge from the same point. |
| It can be viewed on a screen. | It cannot be viewed on the screen. |
| Formed by the concave mirror. | Formed by Convex, Concave, and Plane Mirrors. |
| It is always inverted. | It is always erect. |
Formation of Real Image by Concave Mirror

The image formed by a concave mirror has the following properties:
- It can either be real or virtual.
- It can either be inverted or erect.
- It can have the same size as that of the object, a larger size than that of the object, or a smaller size than that of the object.
The image formed by a convex mirror has the following properties:
- It is always virtual.
- It is always upright (erect).
- It is smaller in size than that of the object
Applications of Convex Mirrors
- The rearview mirrors are convex as they provide a wider view of the road behind.
- Security mirrors near an ATM are convex so that the user can detect easily if anyone else is watching from behind or not.
Applications of Concave Mirrors:
- Satellite dishes use a concave mirror to gather all the signals and reflect them on a certain point.
- Dentists use a concave mirror to reflect light on a particular tooth.
- Shaving Mirrors are concave in shape.
- Headlights of a car have a concave mirror so that we can reflect light straight on the path.
- Torches also use concave Mirrors.
Images Formed by Lenses (VII)
- A lens is a part of a reflecting material like glass or plastic but curved from both sides.
- Lenses are widely used in spectacles, telescopes, and microscopes.
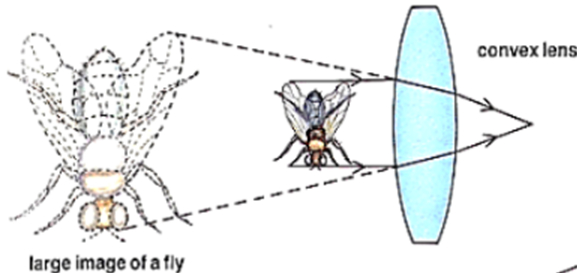
Convex Lens: A Convex Lens is curved outwards. It is thicker in the centre and narrows down at the edges. It merges the light rays passing through it at a certain point. Therefore, it is also called a Converging Lens.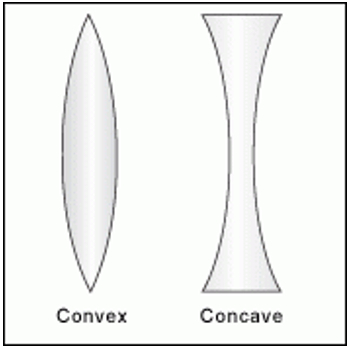
Concave Lens: A Concave Lens is curved inwards. It has wider edges and a thinner centre. It reflects the light that travels through it in different directions. Therefore, it is also called a Diverging Lens.
A Convex lens forms an image that is:
- real
- inverted
- the image is large and appears close to the lens
A Concave lens forms an image that is:
- virtual
- erect
- small and appears far away
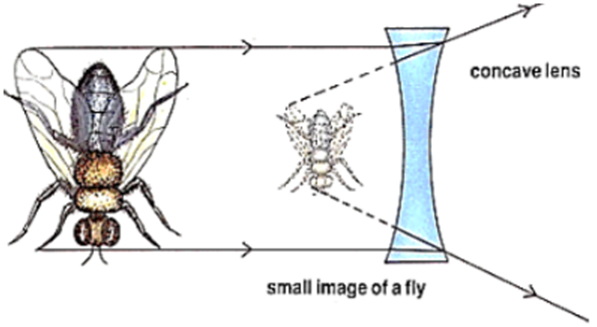
Uses of Concave Lenses
- To see the image of the person standing outside, concave lenses are used in the peepholes in the door of hotel rooms.
- Concave lenses are used in making spectacles.
Uses of Convex Lenses
- Convex lenses are used as magnifying glasses.
- In the manufacturing of spectacles, cameras, microscopes, telescopes, and binoculars, convex lenses are used.
Sunlight - White or Coloured? (VII)
A rainbow is a natural phenomenon in which the light rays of the sun are reflected and refracted by the water droplets present in the atmosphere.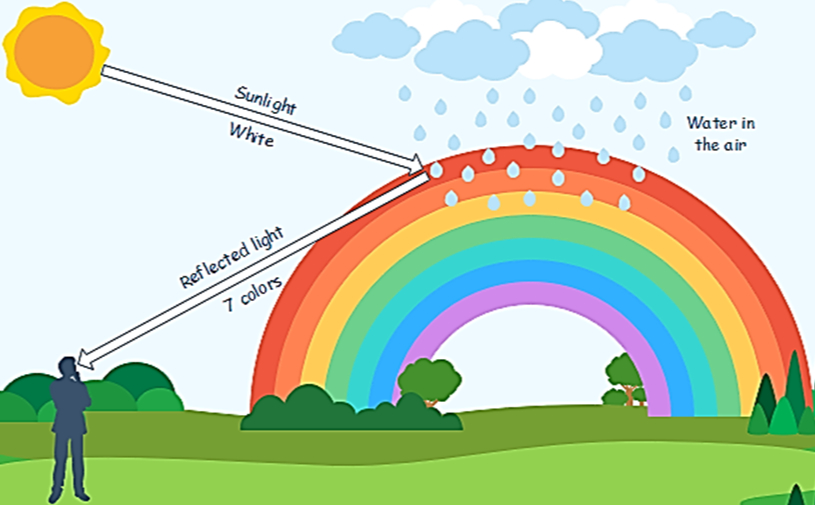
A rainbow appears as an arc in the sky that contains a band of seven colours - Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
The white light of the sun contains seven coloured lights in it that separate out due to refraction called a Spectrum of Lights.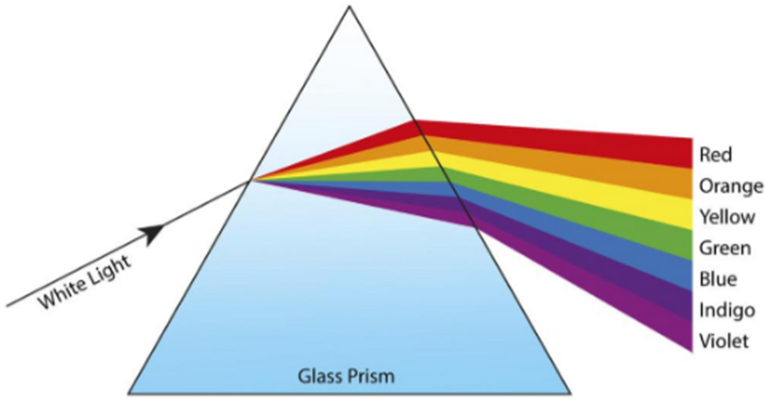
When we blow soap bubbles, they appear colourful.
When light is reflected from the surface of a Compact Disk (CD), we see many colours.
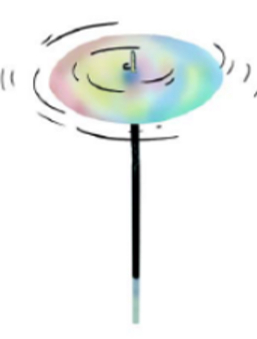
Newton’s disc can be obtained by dividing a disk into 7 partitions and painting each of them with the seven colours of the rainbow.
When Newton’s disc is rotated at a fast pace in daylight all the colours tend to mix and the disc appears whitish in colour.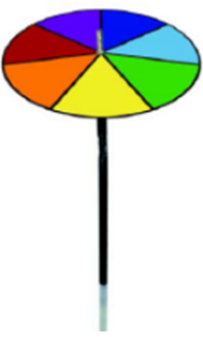



No comments:
Post a Comment