Mode of Nutrition in Plants
Nutrients - Certain substances are present in the foods that help in the survival of the organisms. These special substances are called nutrients, for example, proteins, vitamins, carbohydrates, minerals, and fats.
Nutrition helps to repair damaged parts and organs. Nutrition also provides energy for carrying out various functions.
Modes of nutrition
- Autotrophic
- Hertotrophic
Autotrophs: Organisms that make food themselves are called autotrophs. Plants are an example of autotrophs as they make their own food using carbon dioxide, water, and light energy.
Organisms that rely on others and usually take in ready-made food made by autotrophs are called heterotrophs. Animals and human beings are an example of heterotrophs as they depend on plants in many ways for their food.
Other Modes of Nutrition in Plants
Parasites
- In parasitic mode of nutrition, plants depend on other plants or animals for their nourishment.
- Such dependent plants are called as parasites and the ones on which parasites depend are called as hosts.
- Some examples of parasites are Cuscuta (akash-bel), Cassytha (amar-bel), hookworms, tapeworms, leeches, etc.
Insectivorous Plants
- Insectivorous plants eat living insects for their food hence they are also called carnivorous plants.
- The insectivorous mode of nutrition is observed in plants like the pitcher plant and the Venus fly trap.
- These types of plants purely depend on other insects and small animals for their nutrition.
Insectivorous plants are green and carry out photosynthesis to obtain a part of the food. Pitcher plants trap small insects inside the pitcher and insects are digested by the digestive juices secreted in the pitcher.

Symbiotic plants
- In this mode of nutrition, there is a close association between two different plants of different categories.
- For example, certain fungi live in the roots of trees. In this case, the tree provides nutrients to fungi and in return receives help from it to take up water and nutrients from the soil.
Lichens: Lichens are symbionts. They are white-bluish green crust-like plants growing on rocks or bark of trees. Lichens are very common on hills growing on bare rocks and tree trunks.
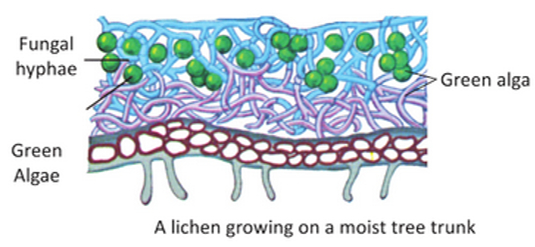
Saprotrophs
The mode of nutrition in which organisms or plants obtain their nutrition from dead and decaying organic matter is called the Saprophytic mode.
The plants which exhibit a saprotrophic mode of nutrition are called saprotrophs. Examples of saprotrophs are moulds, mushrooms, yeasts, and some bacteria.
Saprotrophs secrete digestive juices onto dead and decaying matter to dissolve it and then absorb nutrients from it.
Moulds growing on stale bread and mushrooms growing on moist humus or rotting wood are the fungus plants that are saprophytes.
Fungi and bacteria are known as saprotrophs.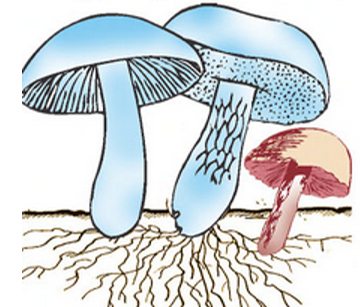
How Nutrients are Replenished in the Soil
Plants get their nutrients from the soil mainly hence there is a need to replenish the soil again with nutrients so that the plants can survive on it.
Fertilizers and manure are often used to replenish the soil with nutrients. They contain potassium, phosphorus, and nitrogen all of which are important for the plants.
A bacterium called Rhizobium is present in the soil which can convert nitrogen present in it into a form that can be consumed by the plants.
The rhizobium generally lives in the roots of the plants such as peas, beans, grams, and legumes and provides nitrogen to these plants. This again is an example of a symbiotic relationship. The farmers often do not need to use fertilizers while growing such crops.
Rhizobium is a type of bacteria that converts atmospheric nitrogen into a soluble form that can be utilized by plants (nitrogen fixation).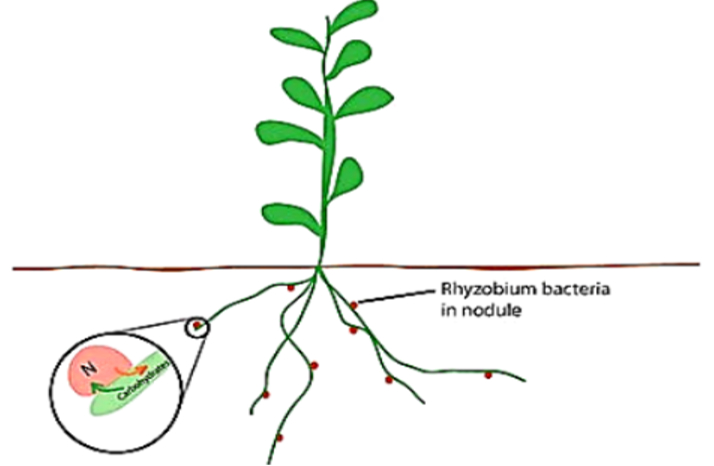
Nitrogen Fixation: The process by which nitrogen is converted into a form that can be used by plants and other living organisms is called nitrogen fixation.
Photosynthesis - food making process in plants
The process by which plants prepare their food by using these raw materials is called Photosynthesis.
The term photosynthesis was given by Charles Reid Barnes in 1893.
The process of photosynthesis can be represented as: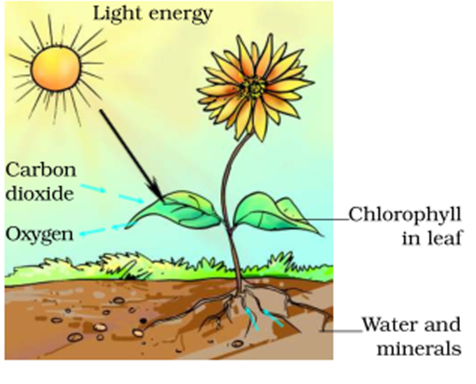
- The process of photosynthesis takes place in the green leaves of a plant.
- The food is prepared by the green leaves of a plant in the form of a simple sugar called glucose.
- The extra glucose is changed into another food called starch. This starch is stored in the leaves of the plant.
- The green plants convert sunlight energy into chemical energy by making carbohydrates.
The process of photosynthesis is completed as follows:![]()
The photosynthesis takes place in the following three steps:
- Absorption of sunlight energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy into chemical energy, and splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen by light energy.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide by hydrogen to form carbohydrates like glucose by utilizing chemical energy.
Conditions necessary for photosynthesis:
- Sunlight
- Chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
Raw materials for photosynthesis:
- Carbon dioxide
- Water
How the plants obtain carbon dioxide?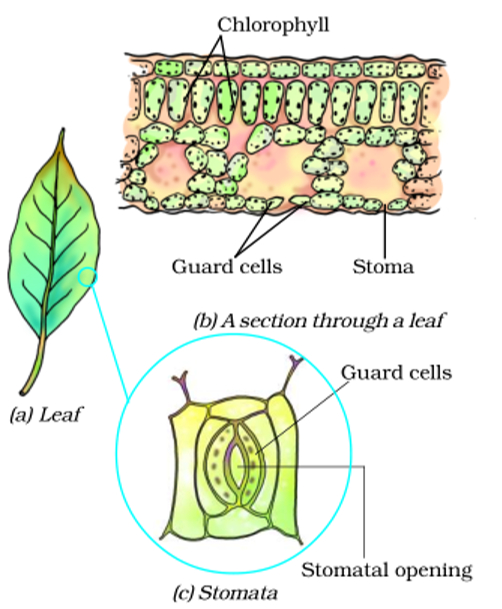
- There are a large number of tiny pores called stomata on the surface of the leaves of plants.
- The carbon dioxide gas enters the leaves of the plant through the stomata present on their surface.
- Each stomatal pore is surrounded by a pair of guard cells. The opening and closing of stomatal pores are controlled by the guard cells
How the plants obtain water for photosynthesis:
- The water required by the plants for photosynthesis is absorbed by the root of the plants from the soil through the process of osmosis.
- The water absorbed by the roots of the plants is transported upward through the xylem vessels to the leaves where it reaches the photosynthetic cells.
- The plants also need other raw materials such as nitrogen, phosphorus, iron, magnesium, etc., for building their body.
- The plants take these materials from the soil.
- Nitrogen is an essential element used by plants to make proteins and other compounds.
Site of photosynthesis: Chloroplasts
- Leaves have a green pigment called chlorophyll.
- It helps leaves capture the energy of the sunlight which is then used to prepare food from carbon dioxide and water.
- Here, you see that solar energy is captured by the leaves and is stored in the plant in the form of food. So, we can say that Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
Glucose (simple carbohydrates) is the simplest food synthesized by plants. This glucose made by plants is converted into complex carbohydrates which are known as starch.
Proteins are nitrogenous substances. Plants prepare proteins with the help of nitrogen which is obtained from the soil.
Photosynthesis is important because
- It provides food to animals including human beings.
- It puts oxygen gas into the air which is essential for breathing and respiration in animals including human beings.
Stoma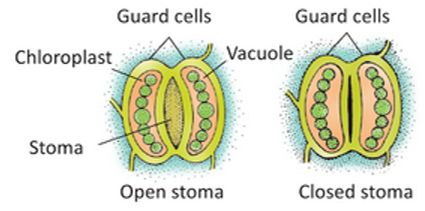
Under normal conditions stomata on green leaves remain closed at night and open during the daytime. Commonly stomata open in the morning and close towards evening.



No comments:
Post a Comment