Physical Changes
Physical Properties of a substance are those characteristics of a substance that describes its physical nature.
Examples of physical properties are colour, density, shape, size and volume are some physical properties.
Physical Change is a change which occurs when there is an alteration in the physical properties of a substance.
The physical change does not result in the formation of any new substance but can alter the shape and size of the existing substance.
Physical Properties: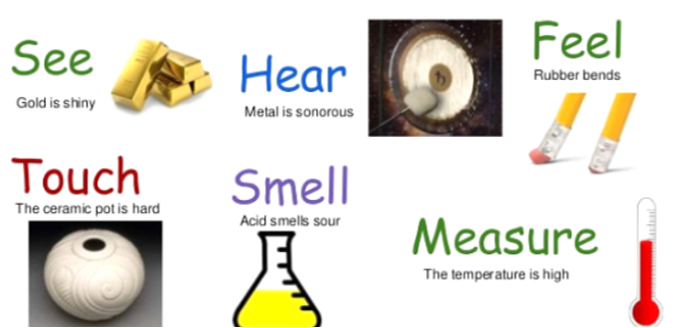
Melting of ice is a physical change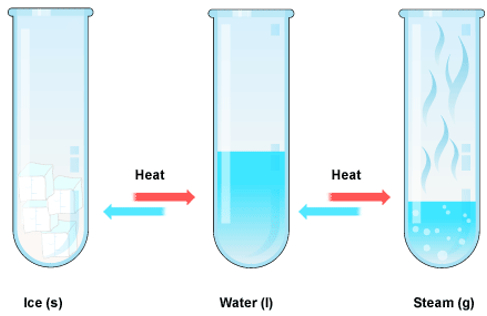
The physical change is generally reversible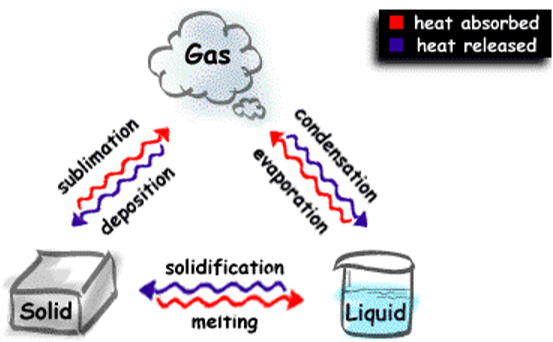
Chemical Change
The chemical property of a substance are that characteristic of a substance that describes its chemical nature. For Example toxicity of a substance or how a substance reacts with other substances is its chemical property.
A chemical change or chemical reaction is any change in the chemical properties of a substance. Whenever a substance undergoes a chemical change, a new substance is formed.
Examples of Chemical Changes:
- Rusting of iron occurs when iron gets in contact with moisture
- When a magnesium ribbon is burnt it radiates white light and converts into ashes
- Extracting of iron from the iron ore
- Formation of plastic
Chemical Properties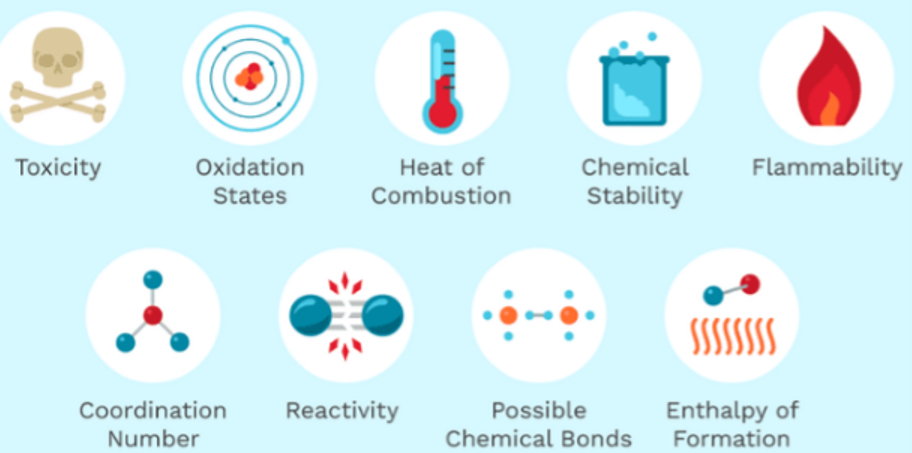
A chemical change is always accompanied by any one or all of the following way:
- Radiation or absorption of heat
- Production of sound
- Change in the colour of the substanc
- Change in the smell of the substance
- Formation of a gas
- Formation of a solid as residue
The characteristics of chemical changes are as follows:
- One or more new substances are formed in a chemical change.
- A chemical change is a permanent change.
- Sound may be produced in a chemical change.
- A permanent change in colour may take place.
- A gas may be formed during the chemical change.
Magnesium (Mg) + Oxygen (O2) 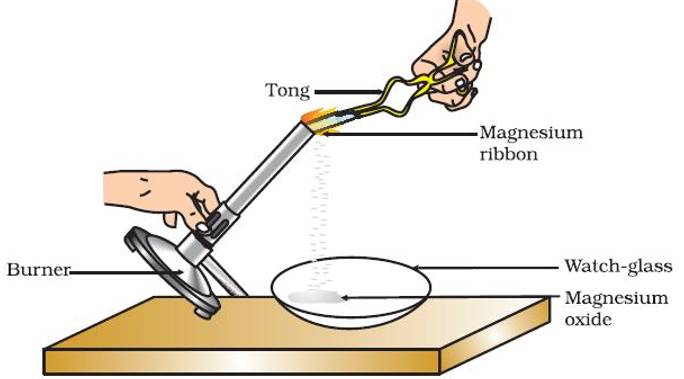
Copper Sulphate Solution (blue) + Iron 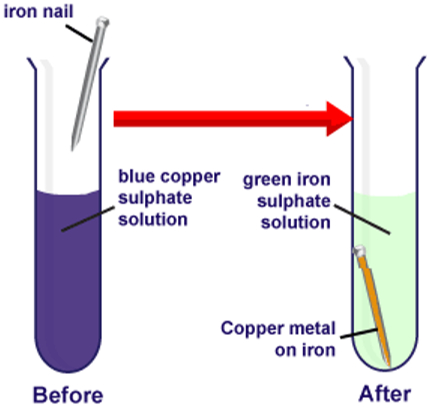
| Physical change | Chemical change |
| Physical changes are mostly reversible. | Chemical changes are not reversible. |
| No new substances are formed. | One or more new substances are formed. |
| The substance retain its chemical properties. | The new substances formed have different properties from the original substance. |
A change or reaction in which heat is released is called an exothermic reaction.
Carbon + Oxygen
A change or reaction in which heat is absorbed from the surrounding is called an endothermic reaction.
Carbon + Sulphur + Heat
Rusting of Iron
When the iron comes in contact with oxygen and water, reacts and forms a red colored substance over it. It is called Rust.
The rusting of iron is a slow continuous process which makes the object useless.
Iron (Fe) + Oxygen (O2, from the air) + water (H2O)
The rusting of iron is a chemical change because iron oxide is formed as a new product.

The following conditions are essential for rusting:
- Presence of oxygen.
- Presence of water or water vapour.
How to prevent rusting of iron
- By applying paint on iron objects so that they cannot come in contact with oxygen and moisture in the environment
- Galvanization of iron which means applying a layer of zinc or chromium metals on the iron.
Crystallisation
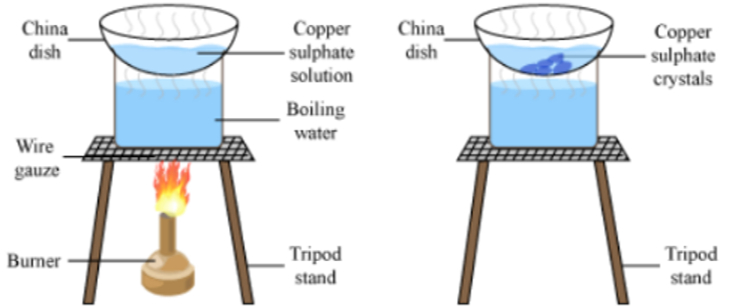
Crystallisation: The process of cooling a hot concentrated solution of a substance to obtain crystals is called crystallization.
Formation of crystals of copper sulphate:
- Take a cupful of water in a beaker and add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid.
- Heat the water.
- When it starts boiling add copper sulphate powder slowly while stirring continuously.
- Continue adding copper sulphate powder till no more powder can be dissolved.
- Filter the solution and allow it to cool.
- Look at the solution after some time to visualize the crystals.
The process of evaporation is not a good technique of separation because of following reasons:
- The soluble impurities do not get removed in the process of evaporation of a salt solution.
- The crystals of salts obtained by the process of evaporation are small and the shape of crystals cannot be seen clearly.




