Modes of Reproduction
Vegetative Parts: These are the parts of the plant that plays a major role in the life cycle of a plant such as the preparation of food, transportation of food, water, nutrients, etc. For Example, roots, stems, and leaves.
Reproductive Parts: These are the parts of a plant that play a major role in the reproduction process of plants, For Example, flowers, and fruits.
Sexual Reproduction: The new plants are produced with the help of the seeds of a plant. In this process, the flowers of the plants participate in reproduction.
Asexual reproduction: The production of new plants from existing plants without the involvement of the gametes is called asexual reproduction. There is no fusion of gametes no seeds are formed in this mode of reproduction. E.g. rose, ginger, potato turmeric, etc.
Shoot: A young plant has often termed a shoot. Generally, a shoot is regarded as a part of the plant which has stems, leaves, and flowers.
Node: It is a part of the stem or branch of a plant from where the leaf arises.
Vegetative Buds: Sometimes buds are present in the leaves that are capable of developing into shoots. These are called Vegetative Buds.
Vegetative propagation: It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves, and buds. Since reproduction is through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known as vegetative propagation.
The plants have stem roots, and leaves which are called vegetative parts of the plant.
Vegetative propagation by stems: The stems bear buds in the axil which produces new plants by the method of cuttings. A smaller part of the stem of a plant that bears buds over it is removed by cutting with a sharp knife is called cutting. Example - rose and Champa.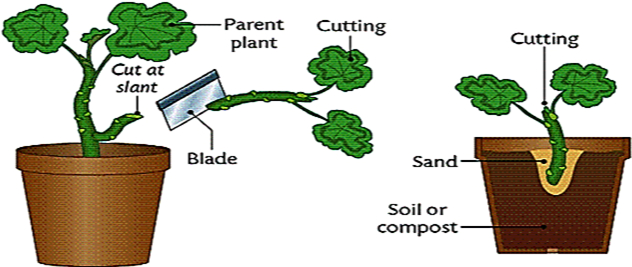
Vegetative propagation by roots: The roots of plants do not bear buds. There are some plants that have modified thickened roots that bear buds. A fresh potato has modified thickened roots with stored food which are called root tubers.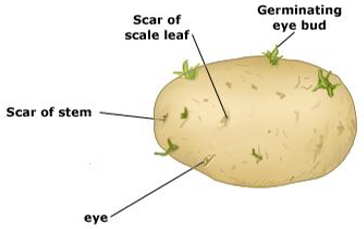
Vegetative propagation by leaves: The leaves of some plants develop buds on them. These leaves having buds can be used as structures of vegetative reproduction in plants. For e.g. Bryophyllum, Begonia is a plant that grows by vegetative propagation by leaves.
Advantages of vegetative propagation:
- Plants produced by vegetative propagation take less time to grow and bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- The new plants produced by vegetative propagation are exactly like the parent plant.
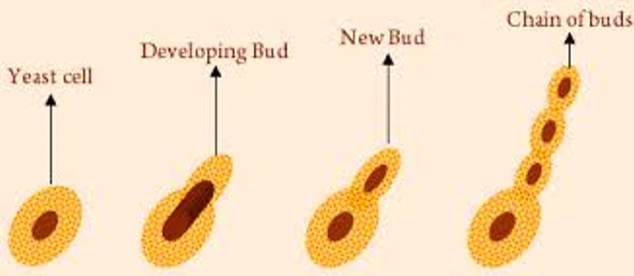
Budding: It is an asexual method of reproduction, a small part of the body of the parent plant grows out as a bulb-like projection called bud which then detaches and becomes a new plant. For e.g. yeast is a single-celled organism that grows by budding.
The small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is called a bud. The bud gradually grows and gets detached from the parent cell and forms a new yeast cell. The new yeast cell grows, matures, and produces more yeast cells.
Fragmentation: The breaking up of the body of a plant into two or more pieces on maturing each of which subsequently grows to form a new plant is called fragmentation. The breaking up of the body of the parent plant in fragmentation to form new plants occurs naturally when the parent plant matures. Example - alga and spirogyra.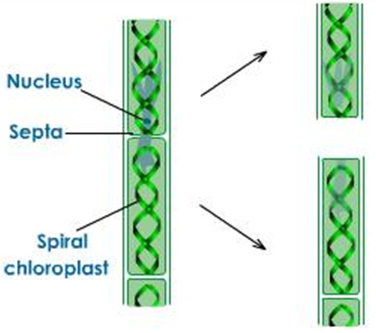
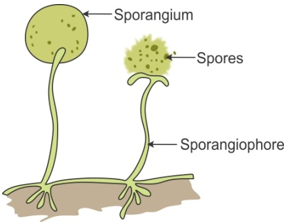
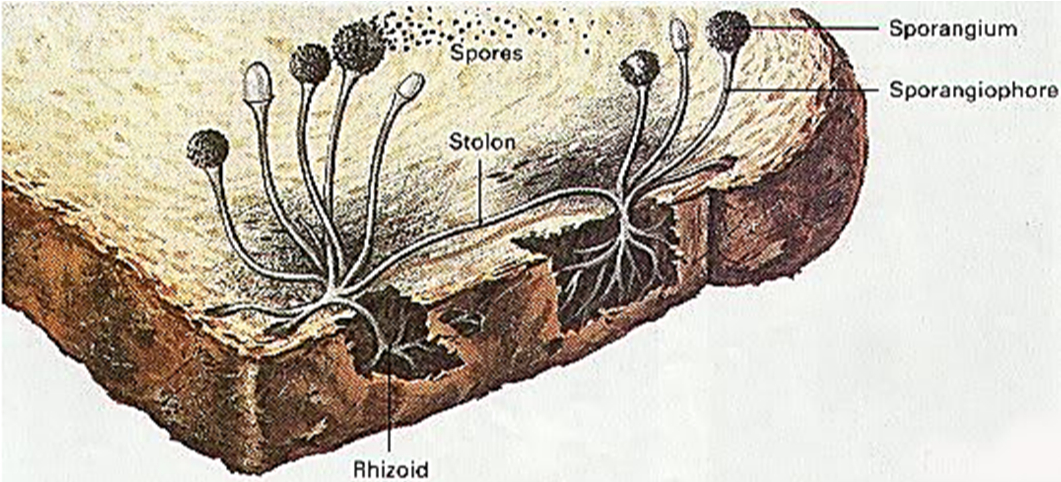
Spore formation:
- A spore has a hard protective cover that protects it from unfavorable environmental conditions like temperature and humidity.
- As a result, the spores can travel long distances and survive for a long duration of time.
- As soon as they find favorable conditions such as moisture and nutrients, they germinate and form new plants.
- For Example, Moss and ferns propagate in this way.
Runners: Some plants grow along the ground and contain modified stems called Runners. These runners contain buds that can produce roots and stems. Example: Strawberries.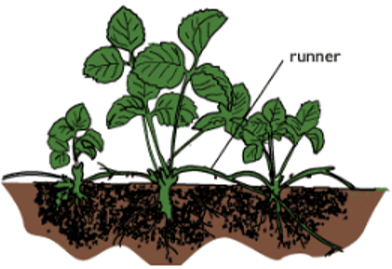
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction: The production of new plants from existing plants by fusion of their gametes is called sexual reproduction. Flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant
The stamens are the male reproductive part and the pistil is the female reproductive part.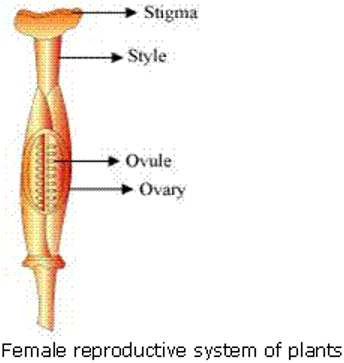
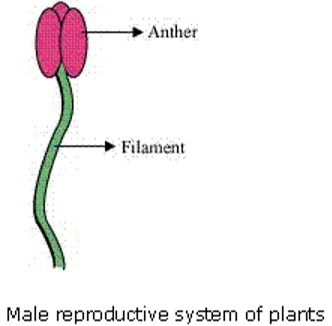
The base of a flower to which all parts of a flower are attached is called receptacle.
The green leaf like parts in the outermost circle of a flower is called sepals.
All the sepals taken together are called calyx.
The colorful parts of a flower are called petals.
The petals lie inside the sepals.
All the sepals taken together are called corolla.
The flowers which contain only one reproductive organ are called unisexual flowers like watermelon, corn.
The flowers which contain both reproductive organs are called bisexual flowers like hibiscus and petunia.
The pistil consists of three parts: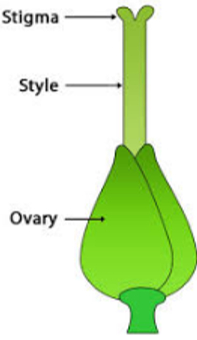
- Stigma: It is a sticky surface where pollen grains get attached.
- Style: It is a tube-like structure which connects the stigma and the ovary.
- Ovary: It contains eggs in which the female gametes or eggs are formed.
Pollination: Pollination is the process by which pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma of the plant, thereby enabling fertilization and reproduction. It is unique to the angiosperms, the flower-bearing plants.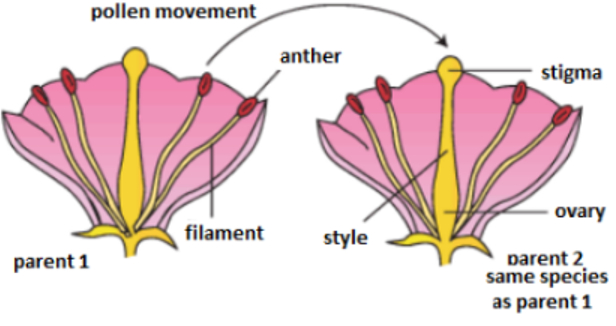
Self-pollination/ Autogamy: When the pollen grains land on the stigma of the same flower.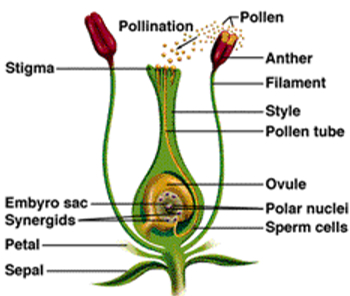
Cross-pollination/ Xenogamy: When the pollen grains land on the stigma of a different flower, whether of a similar kind or a different kind.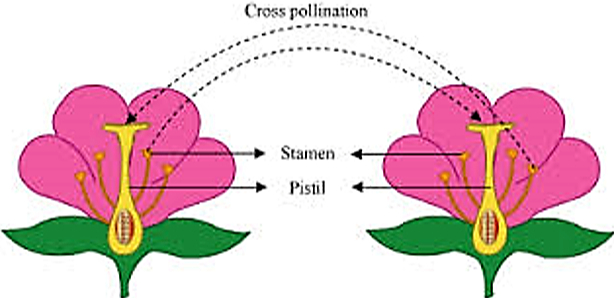
The blowing wind carries pollen grains from one flower to other flowers and helps in pollination.
Fertilization: The cell which results after the fusion of the gametes is called a zygote. The process of fusion of male and female gametes (to form a zygote) is called fertilization
Agents of Pollination: The process of pollination is carried out by some external agencies like wind, water, insects, birds, etc. These are called agents of pollination.
Fruits and Seed Formation
Formation of Fruits and Seeds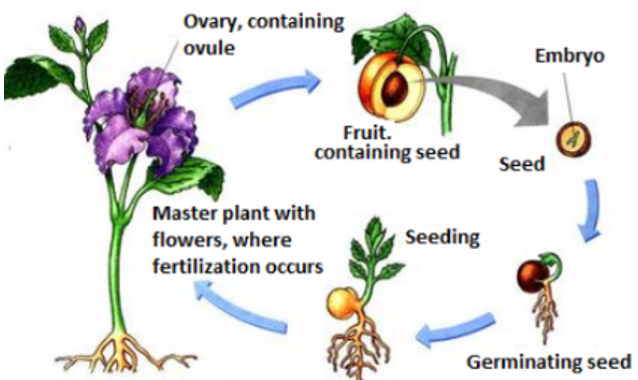
The seeds contain embryos and food for developing new plants. There is a tough protective coating around the seed which is called the seed coat.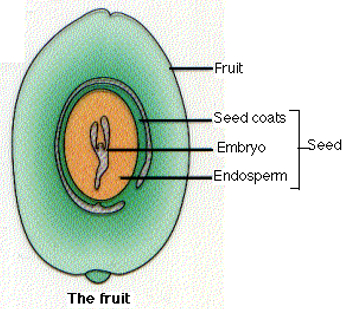
Germination of Seed: A seed contains a plant embryo in a resting state which begins to grow only under favourable conditions. The process by which seeds begin to grow is called seed germination.
Seed Dispersal
Seed dispersal: The transportation of seeds from the parent plant to different places is called seed dispersal. Seed dispersal allows the growth of the same kind of plants in different regions.
Winged seeds such as those of drumstick and maple light seeds of grasses or hairy seeds of aak (Madar) and the hairy fruit of sunflower get blown off with the wind to faraway places.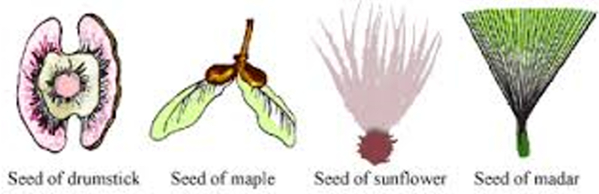
Some seeds are dispersed by water. These fruits or seeds usually develop floating ability in the form of the spongy or fibrous outer coat as in coconut and lotus.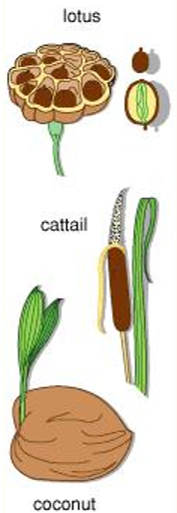
Some seeds are dispersed by animals, especially spiny seeds with hooks that get attached to the bodies of animals and are carried to distant places. Examples are Xanthium and Urena.
Some seeds are dispersed when the fruits burst with sudden jerks. The seeds are scattered far from the parent plant. This happens in the case of castor and balsam.
Benefits of Seed Dispersals
- Seed dispersal avoids overcrowding of young plants around their parent plants.
- It helps in preventing competition between the plants and their own seedlings for sunlight, water, and minerals.
- One of the benefits of seed dispersal is that it enables the plant to grow into new habitats for wider distribution and provides them with a better chance of survival.




No comments:
Post a Comment