Circulatory System
Blood: It is a red-colored liquid that flows in blood vessels and circulates in our bodies. It is red in colour as it contains a red pigment called hemoglobin which is responsible to carry oxygenated blood to the cells and removing carbon dioxide from the blood.
Blood consists of four components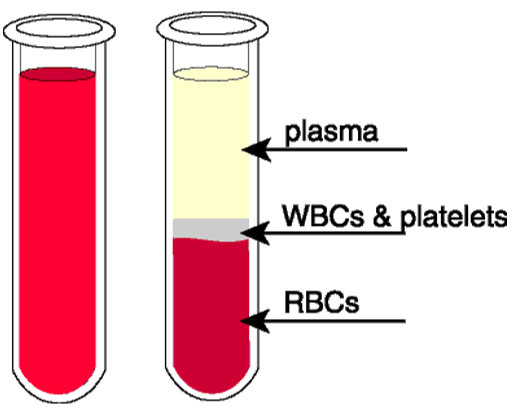
- Plasma
- Red blood cells (RBCs)
- White blood cells (WBCs)
- Platelets
Plasma: Blood plasma is the pale yellow liquid component of blood that normally holds the blood cells in whole blood in suspension and this makes plasma the extracellular matrix of blood cells. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is 90% water and 3.5% common salt.
Red blood cells (RBCs): The red coloured cells which contain red pigment hemoglobin is called red blood cells. They are also called erythrocytes. Red cells carry oxygen from the lungs to all the cells of the body. Hemoglobin binds with oxygen and transports it to all the parts of the body and ultimately to all the cells. These cells lack a cell nucleus and most organelles to accommodate maximum space for hemoglobin.
White blood cells (WBCs): White blood cells (WBC), also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious diseases and foreign invaders. Some white cells eat up the germs which cause disease. These cells make chemicals called antibodies to fight against infections.
Platelets: Platelets are tiny cells found in the blood. Platelets are also called thrombocytes. They have no cell nucleus. They help in stopping the bleeding by clumping and clogging blood vessel injuries.
Functions of Blood:
- Blood carries water to all parts of the body.
- Blood removes carbon dioxide from the blood cells to the lungs for breathing out.
- Blood carries a waste product urea from the liver to the kidneys for excretion in urine.
- Blood protects the body from disease as the white blood cells kill the bacteria and other germs which cause diseases.
Blood Vessels: Our body contains tube-like structures called blood vessels that help in the transportation of blood throughout our body. There are different types of blood vessels in the body like arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Arteries: Arteries have elastic and thick walls. They carry blood from the heart to all the parts of the body. The arteries are found quite deep under the skin and they are not seen easily.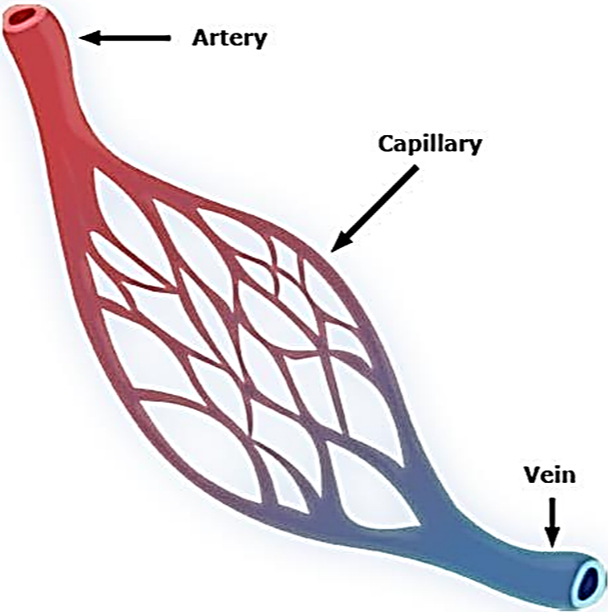
Veins: Veins are the blood vessels that carry blood from all the parts of the body to the heart. These vessels carry blood toward the heart. The veins are less deep than arteries and could be seen easily.
Capillaries: Capillaries are extremely thin blood vessels that connect arteries to veins. Capillaries are always present in between the arteries and veins in our body. Every cell of the body is near a capillary.
Pulse rate: To know the pulse rate of a person, place the middle and index finger of your right hand on the inner side of your left wrist. Count the number of pulse beats in one minute. The resting person usually has a pulse rate between 72 and 80 beats per minute.
The circulatory system consists of blood, blood vessels, and the heart.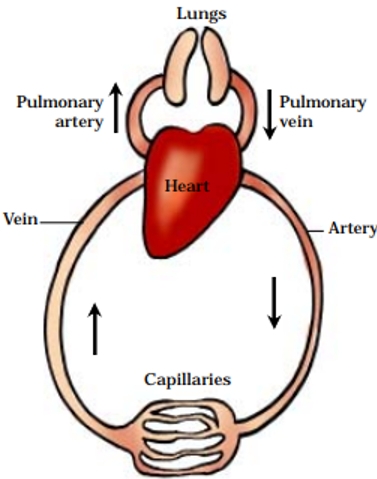
The Heart
- It is located in the chest cavity.
- Its lower part is a little tilted towards the left.
- The heart is divided into four chambers to prevent the oxygen-rich blood from mixing with carbon dioxide-rich blood.
- The Atria or upper chambers contain the blood with no oxygen.
- The Ventricles or the lower chamber of the heart contains oxygen-rich blood.
- The Atria and Ventricles both are individually divided within themselves into two chambers with the help of valves.
- From the left ventricle, the biggest artery of our body called the aorta begins.
- The right Atrium of the body receives deoxygenated blood from the body through a vein called the Vena cava. The Vena cava is the largest vein of our body.
The heart is an organ that beats continuously to act as a pump for the transport of blood, which carries other substances with it.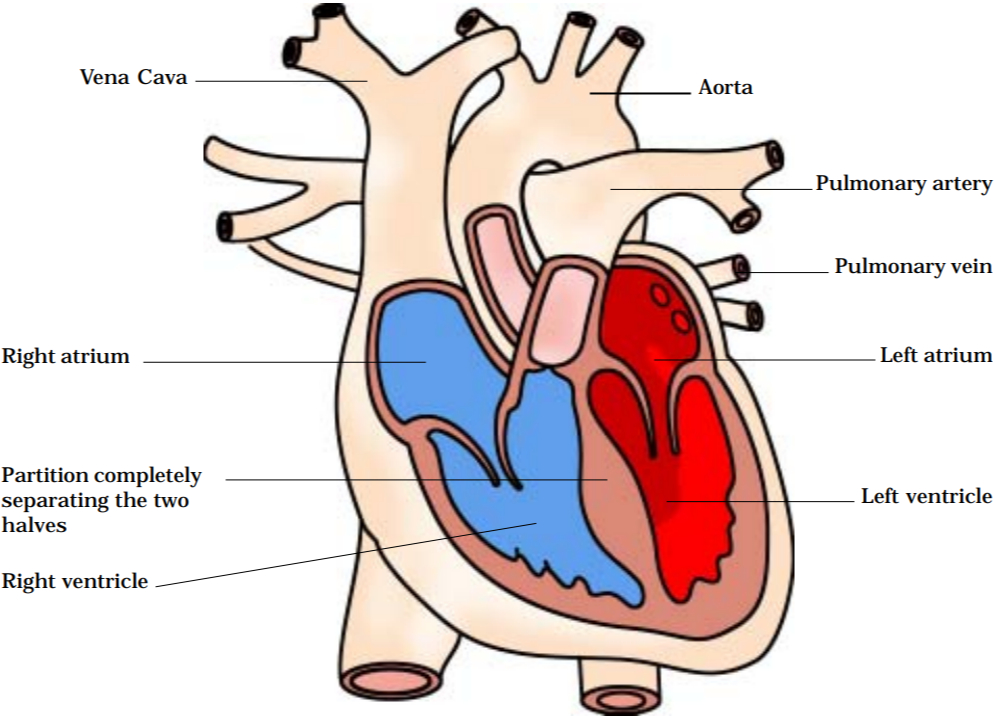
The flow of Blood in the Human Body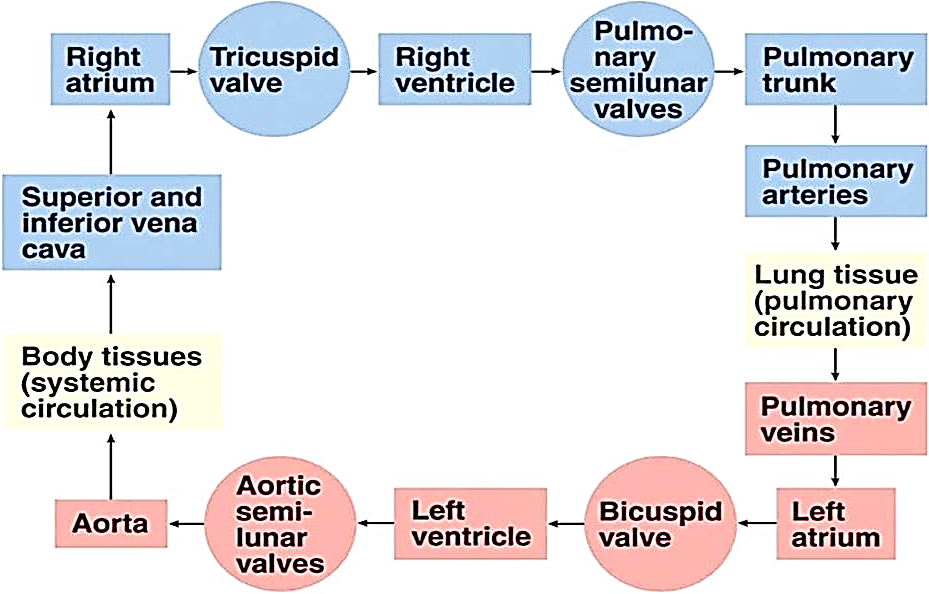
Heartbeat: The muscles of the heart relax and contract continuously as it pumps the blood in the arteries. This rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart are called a heartbeat.
Stethoscope: The stethoscope is an instrument that is used to listen to the Heartbeat of a person. It amplifies the Heartbeat so that the doctors can monitor it and find out about the patient's condition.
Stethoscope: It contains two earpieces, and a tube that connects them to a chest piece comprising of a sensitive diaphragm.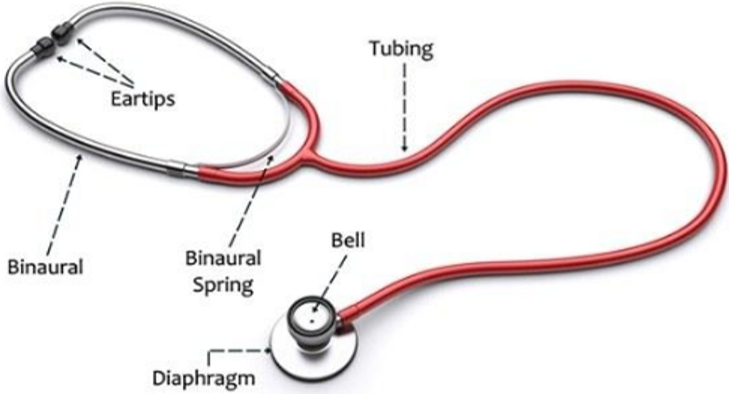
Do all animals possess a circulatory system?
- No, animals like Hydra and Sponges do not possess a circulatory system.
- These animals live in water and hence get food and oxygen from the water as it enters their bodies.
- As the water comes out of their bodies, it takes away carbon dioxide and waste materials.
Excretion in Animals
The removal of waste materials produced in the cells of living organisms is called excretion.
Human excretory system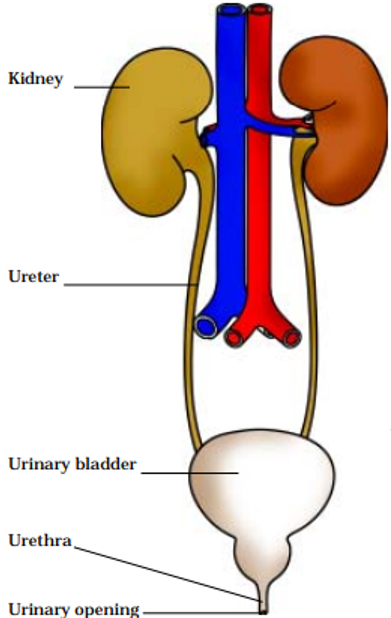
Kidneys: there are two organs called Kidneys present in our body. These Kidneys contain blood capillaries that filter out the unwanted substances from the blood in the form of urine.
Urinary bladder: The urine produced by the Kidneys is stored in a bladder called the urinary bladder.
Ureters: There are two tube-like structures that connect the Kidneys and the urinary bladder. They allow the passage of urine from the kidney to the bladder.
Urethra: There is a muscular tube through which the urine moves out of the body.
The major excretory product in humans is urea. The urine consists of toxic wastes (2.5%), urea (2.5%), and water (95%).
The way in which waste chemicals are removed from the body of the animal depends on the availability of water.
Fishes and aquatic animals excrete ammonia in the water.
Birds, Snakes, and lizards excrete semi-solid, white-coloured uric acid.
Dialysis: Sometimes people use artificial Kidneys, that is, they get the blood purified artificially periodically. It is called dialysis. They have to do so in a case of Kidney failure in which the Kidneys of a person are unable to perform their function due to an infection or an injury.
How is sweat useful to us?
- Sweat contains water and some salts and hence helps in getting rid of toxic wastes from the body.
- Also, as the sweat evaporates from our skin, it takes up our body heat and this makes us feel cool, especially during the summer days.
Transport of Substances in Plants
Transport of Substances in Plants: Plants take up water and dissolved minerals from the soil through their roots and transport them to their leaves. The leaves use this water and mineral for synthesizing their food by the process called photosynthesis. The food produced by green plants is transported back to all the parts of the plant body.
Transport of Water and Minerals: Plant root absorbs water and mineral from the soil. The roots possess root hair which increases the surface area of the root for absorption of water and minerals nutrient that is dissolved in the water. It is moved from roots up to the stem and leaves through the tube-like tissue called as xylem.
The absorption and flow of water is a continuous process through the xylem tissue. Xylem tissues are the continuous network of channels that connect roots to the leaves through the stem and branches. It thus transports water and minerals to the leaves of the entire plant.
Transport of Food Material: The food manufactured in the leaf is transported to different parts of the plants. This transportation of food material from leaves to the other parts of plants is carried out by the tissue called phloem and the process of transport of food material is called translocation. The phloem consists of vessels that are known as sieve tubes.
Xylem: It is a vascular tissue that is responsible for transporting nutrients and water in plants. The root cells absorb water and minerals and transport them to the xylem. Xylem carries it to other parts unidirectionally without the usage of energy.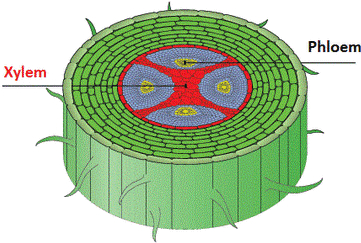
Phloem: It is a vascular tissue that transports the food produced by the leaves (source) to all parts of the plant (sink). This flow is bidirectional and utilizes energy. This is known as translocation.
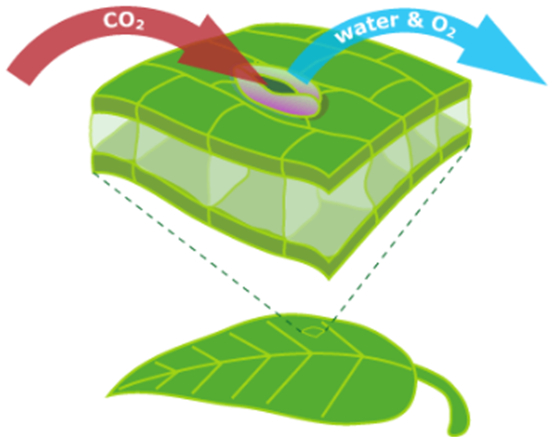
Transpiration: The evaporation of water from the leaves of plants is called transpiration. It is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves but also from stems and flowers.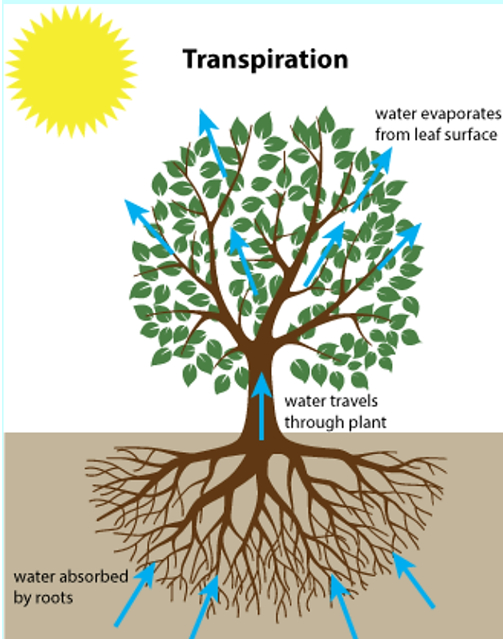
Transpiration results in the absorption of water: As the water from the leaves evaporates, it generates a suction pull in the plants that bring the water from the roots upwards.
Transpiration helps in cooling down the plants: As the water evaporates, it utilizes the heat of the plant and results in cooling the internal temperature of the plant.
The process of evaporation of water through the stomata present on the surface of leaves is called transpiration.