Visit To A Forest
Forests are called the green lungs of nature as they release oxygen during the process of photosynthesis. This oxygen is used up by animals including man for respiration. Thus forests maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The upper part or top of a tree is called its Crown.
A forest has different types of plants like herbs, shrubs, and trees. It also has many types of tall grasses, canes, creepers and climbers.
Stratification in Forests: Stratification is defined as dividing a natural habitat into several layers depending upon the heights of plants or vegetation in that area. This allows minimization of competition among the animals and allows them to survive easily.
The Herb Layer: It consists of plants without woody stems that grow above the ground such as grasses. They are usually less in number in the forests.
The Forest Floor: It comprises the shed leaves, stems, bark, and the top layer of soil.
Canopy: The uppermost branches and leaves of tall trees which act as a roof over the forest ground is called the canopy. It is the highest layer of vegetation in the forest. The branch part of a tree above the stem is known as the crown of the tree.
The Shrub Layer: It consists of plants of small to medium sizes. This layer requires the most sunlight.
The Emergent Layer: It consists of the topmost layer of trees. It is generally found in tropical forests.
Understorey: The different horizontal layers formed due to different types of crowns in the forest is called understorey.
Components of the Forest: The living organisms found in the forest are plants, animals, decomposers, and scavengers. The non-living environment of the forest provides nutrients, water, and carbon dioxide for the growth of the plants.
Plants: Green plants are living organisms also called autotrophs as they produce food by photosynthesis (by absorbing nutrients water from the soil, CO2 from the air, and sunlight as an energy source). They provide food to all living organisms which live in the forest. They are called producers (of food).
Animals: Forests have many animals and they are called consumers (of food). The animals which eat only plants/their parts are called herbivores (herb eating) whereas flesh-eating animals are called carnivores. All animals are called heterotrophs because they depend on other organisms for food.
Decomposers: Mostly these organisms are microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. They feed on dead plants and animals and thus are called saprotrophs. These organisms are also called decomposers as they break down dead parts of plants and dead bodies of animals into simple substances.
Scavengers: Those animals which eat dead animals are called scavengers, e.g. vultures, crows, jackals, hyena, some insects (ants, beetles, termites, woodlice, maggots, millipedes, and earthworms), etc. Scavengers are the cleaning agents of our environment. But these are not decomposers as they do not break down complex dead organic matter into simple ones.
Humus: It is a dark-colored substance found in the soil. Humus is made from dead and decaying organisms. The microorganisms live upon the decaying matter and convert it to humus.
The trees that are not as tall as canopy trees, form different layers or tiers under the canopy are called understoreys.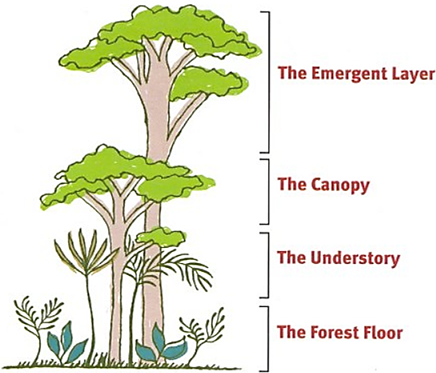
Importance of forests:
- Plants purify the air by utilizing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. They also maintain a balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide and prevent global warming on earth.
- They provide food to wild animals directly or indirectly. Herbivores eat plants and carnivores prey upon herbivores.
- They provide useful materials like firewood, timber, bamboo, wood for paper, gum, resin, fiber, honey, bee wax, bidi leaf, etc. They also provide spices like black pepper, cardamom, cinchona, cinnamon, etc.
- Plants are a source of many medicines. Ayurvedic medicines are prepared from medicinal plants like tulsi, neem, jamun, turmeric, ginger, etc.
Living things and their environment together form an ecosystem. The living components of an ecosystem are producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Producers: All producers are autotrophs because they make food for all non-green living organisms on earth. Example - green plants.
Consumers: Animals and non-green plants obtain nutrients from green plants and are called consumers. Consumers are heterotrophs. They are divided into three types – herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores.
Herbivores: Herbivores eat plants and plant products. Example - cow, goat, camel, elephant, etc.
Carnivores: Carnivores are flesh-eating animals. They prey upon herbivores. Examples – tiger, lion, fox, hawk, etc.
Omnivores: Omnivores eat both plants and animals. Examples - man, crow, bear, etc.
Food chain can be defined as a sequence of living organisms in which one organism feeds on another.
- A typical chain in grassland is: grass
deer lion - A typical food chain in a pond is: algae
small fish large fish
Food chain: The producers, consumers, and decomposers are connected in the ecosystem where one organism eats another which in turn is eaten by the third one.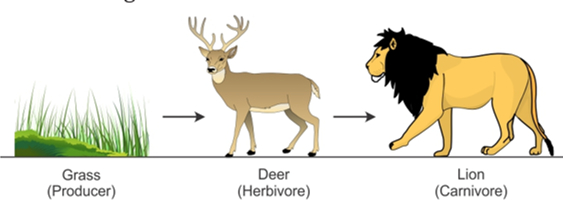
Food web: A food web is a complex feeding system in which several food chains are interlinked.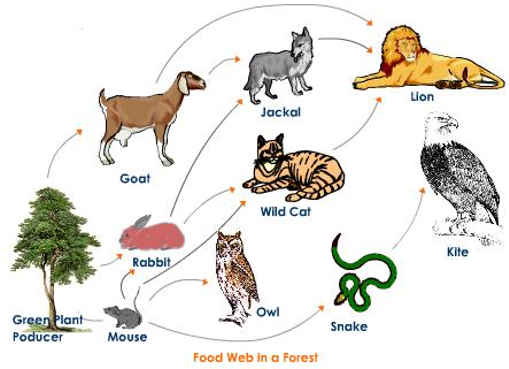
- Carbon dioxide for photosynthesis which animals release during respiration.
- Pollination of flowers for seed formation.
- Dispersal of seeds and fruits to new places to avoid overcrowding of seedlings in one place.
- Nutrients in the form of inorganic salts by recycling.
Dependence of animals on plants:
- Food is obtained by eating leaves, fruits, seeds, nuts, etc. to obtain energy.
- Oxygen needed for respiration is obtained from plants during photosynthesis.
- Shade and protection are provided by large trees.
- Trees provide shelter to birds and some other animals.
Human beings get the following things from plants:
- Food and natural fibers like cotton, jute, etc.
- A variety of wood products like timber, wood for paper, and pulp.
- Oils like pine oil, khus and sandalwood oil, etc.
Threats to forests: Deforestation and pollution are the two major threats to forests.
Deforestation: The large-scale felling of trees is called deforestation. It leads to the permanent destruction of forests.
Causes of deforestation:
- Increased demands of fuelwood and wood for paper and timber.
- Increased demand for land for industries, houses, roads, railway tracks, and other transport facilities.
- Increased mining activity.
- More land for agriculture to provide food for the increasing human population.
- Overgrazing by cattle and sheep.
- Lowering the water table causes plants and trees to wilt and die.
Consequences of deforestation:
- An increase in the overall temperature of the earth is called global warming.
- Lesser rain causes desertification.
- Increased soil erosion leads to loss of humus from the soil.
- An unbalanced ecosystem leads to depleted groundwater and disturbed oxygen and carbon dioxide ration in the atmosphere.
Why forests are called green lungs?
- We know that plants take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
- Hence the plants in the forests provide oxygen to the animals and their animals provide carbon dioxide to the plants.
- In this way, a balance of Oxygen and Carbon dioxide is maintained in the atmosphere in forests. This is a reason why forests are called Green Lungs.
Forests preserve the water cycle:
- We know that plants get rid of excess water through the process of transpiration.
- In this process, the water is released as water vapour into the atmosphere.
- Hence forests increase the water vapour content in the atmosphere.
- This water vapour condenses and forms clouds which lead to increased rainfalls in the area.




No comments:
Post a Comment